
查询语句写了limit 1,为什么依然很慢?
问题背景
最近使用华为图引擎GES, 有一条cypher语句携带后缀limit 1,理论上应该很快返回结果,可是跑了很久依旧没有返回,简化后的语句如下:
match(v)-[r1:dependency *1..1]->(node) where node.product_name = "product" match path = (m)-[r:dependency*0..10]-> (v:Material) return path, m,node skip 0 limit 10调整limit 10至limit 1,结果依旧很慢。
在华为云图引擎GES官网文档上,发现了对查询语句进行终止的接口:
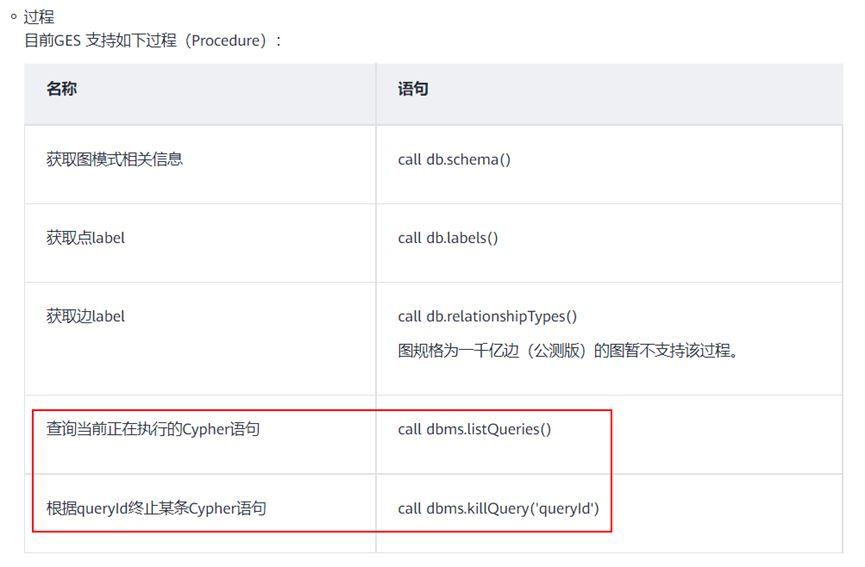
首先使用listQueries查询出当前cypher语句的queryId,然后把queryId输入killQuery中终止慢查询。
问题分析:为什么limit配置为1,依旧长时间无结果?
在华为云图引擎控制台,使用explain打印cypher查询计划,分析慢查询生成原因,简化后的查询计划如图:
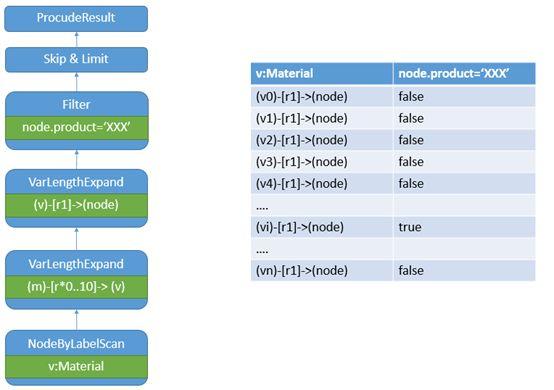
可以看到,查询语句的执行和预期有差异。查询语句优先执行了一个Label扫描算子(NodeByLabelScan),对扫描到的每个点按入边方向进行了[r*0..10]这样的10跳操作,而后再从出边方向做了一跳并过滤,这就导致了最坏情况下,需要全图Label为Material的点都跳完10跳,才能拿到一条结果。如上图表格所示,在遍历到第一个满足条件的(vi)之前,已经对(v0)到(vi)这些点都做了10跳。即使语句末尾写了limit 1,因为始终遍历不到合适的数据,导致了后台的计算引擎一直在做计算。
估计计算引擎在读取这条语句时,同时看到了v:Material和node.product='xxx'两个过滤条件,而代价估计模型认为v:Material可以获得更低的代价,所以才选择优先执行NodeByLabelScan。
使用语句优化策略对语句进行优化
既然分析清楚了原因,那么只要通过改写cypher语句,让GES的cypher不优先通过v:Material做计划即可。这里用到下列两类策略:
with别名策略:使用with为变量安排别名,强制规定语句不同子句的执行顺序
label过滤改写策略:将label过滤条件放在where语句中,并使用labels函数,防止生成NodeByLabelScan的计划
使用with别名策略后,语句如下:
match(v0)-[r1:dependency *1..1]->(node) where node.product_name = "product" with v0 as v,node match path = (m)-[r:dependency*0..10]-> (v:Material) return path, m,node skip 0 limit 10使用label过滤改写策略,语句如下:
match(v)-[r1:dependency *1..1]->(node) where node.product_name = "product" match path = (m)-[r:dependency*0..10]-> (v) where labels(v)='Material' return path, m,node skip 0 limit 10两种策略混合使用,语句如下:
match(v0)-[r1:dependency *1..1]->(node) where node.product_name = "product" with v0 as v,node match path = (m)-[r:dependency*0..10]-> (v) where labels(v)= " Material" return path, m,node skip 0 limit 10使用explain将三种查询计划分别打印,如图:
本文系作者在时代Java发表,未经许可,不得转载。
如有侵权,请联系nowjava@qq.com删除。
