如果线程在等待时接到通知,但线程等待的条件还不满足,此时,线程接到的就是早期通知,如果条件满足的时间很短,但很快又改变了,而变得不再满足,这时也将发生早期通知。这种现象听起来很奇怪,下面通过一个示例程序来说明问题。
很简单,两个线程等待删除 List 中的元素,同时另外一个线程正要向其中添加项目。代码如下:
import java.util.*;
public class EarlyNotify extends Object {
private List list;
public EarlyNotify() {
list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList());
}
public String removeItem() throws InterruptedException {
print("in removeItem() - entering");
synchronized ( list ) {
if ( list.isEmpty() ) { //这里用if语句会发生危险
print("in removeItem() - about to wait()");
list.wait();
print("in removeItem() - done with wait()");
}
//删除元素
String item = (String) list.remove(0);
print("in removeItem() - leaving");
return item;
}
}
public void addItem(String item) {
print("in addItem() - entering");
synchronized ( list ) {
//添加元素
list.add(item);
print("in addItem() - just added: '" + item + "'");
//添加后,通知所有线程
list.notifyAll();
print("in addItem() - just notified");
}
print("in addItem() - leaving");
}
private static void print(String msg) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + ": " + msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final EarlyNotify en = new EarlyNotify();
Runnable runA = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
String item = en.removeItem();
print("in run() - returned: '" +
item + "'");
} catch ( InterruptedException ix ) {
print("interrupted!");
} catch ( Exception x ) {
print("threw an Exception!!!\n" + x);
}
}
};
Runnable runB = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
en.addItem("Hello!");
}
};
try {
//启动第一个删除元素的线程
Thread threadA1 = new Thread(runA, "threadA1");
threadA1.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
//启动第二个删除元素的线程
Thread threadA2 = new Thread(runA, "threadA2");
threadA2.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
//启动增加元素的线程
Thread threadB = new Thread(runB, "threadB");
threadB.start();
Thread.sleep(10000); // wait 10 seconds
threadA1.interrupt();
threadA2.interrupt();
} catch ( InterruptedException x ) {}
}
} 执行结果如下:
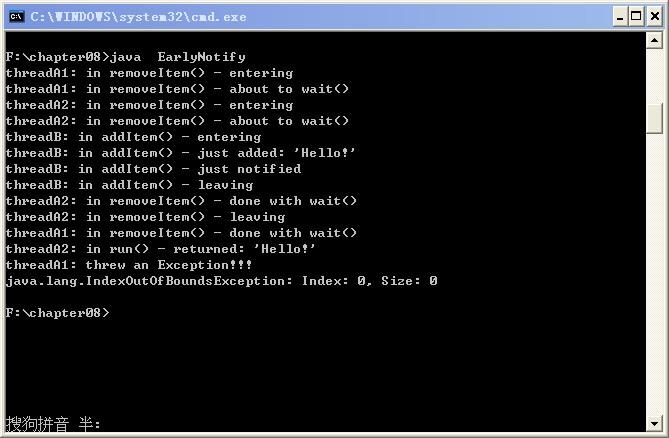
分析:首先启动 threadA1,threadA1 在 removeItem()中调用 wait(),从而释放 list 上的对象锁。再过 500ms,启动 threadA2,threadA2 调用 removeItem(),获取 list 上的对象锁,也发现列表为空,从而在 wait()方法处阻塞,释放 list 上的对象锁。再过 500ms 后,启动 threadB,并调用 addItem,获得 list 上的对象锁,并在 list 中添加一个元素,同时用 notifyAll 通知所有线程。
